What Is Crypto Mining? How It All Works
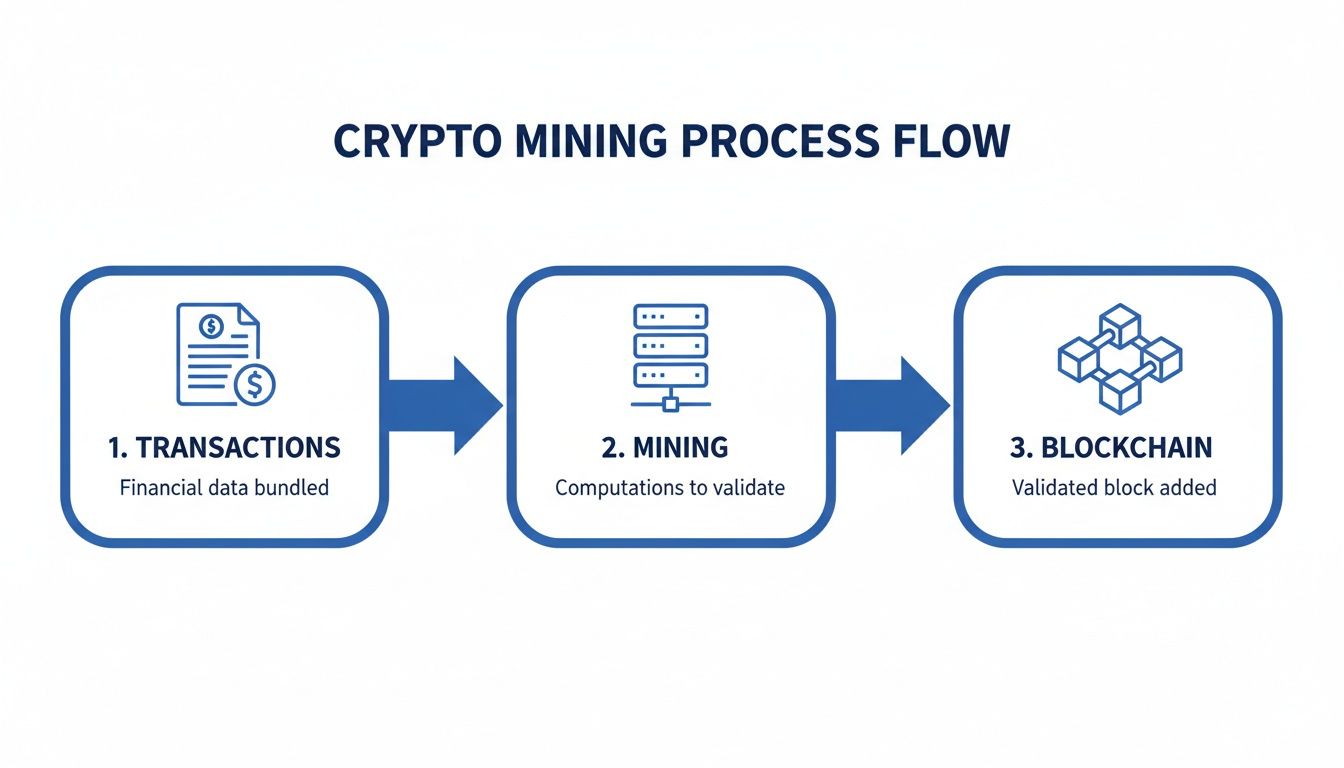
Let’s be blunt: crypto mining is the process of creating new digital coins and verifying transactions. Think of it as a massive, decentralized lottery. All over the world, powerful computers are in a constant race to solve incredibly complex math puzzles. The first one to crack the code gets the prize: the right to update the official transaction ledger (the blockchain) and a reward in the form of brand-new cryptocurrency.
In short, mining is the engine that powers and secures many of the world’s most popular cryptocurrencies.
A Simple Look at Crypto Mining
At its heart, mining is what keeps cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin running securely. Instead of a bank or a government overseeing everything, that responsibility is handed over to a global network of volunteers called “miners.”
This is the key difference that sets crypto apart. There’s no middleman. The power and the work of keeping the system honest are distributed among everyone participating in the network.
The Role of a Crypto Miner
So what does a miner actually do? Think of them as digital bookkeepers with a competitive streak. They have two critical jobs:
- Verifying Transactions: When you send crypto to someone, a miner scoops that transaction up with a bunch of others into a list, known as a “block.” Their first job is to ensure every transaction in that block is legitimate and that no one is trying to spend the same digital coin twice.
- Securing the Network: This is where the race begins. Miners use their powerful computers to solve a complex mathematical puzzle tied to that block of transactions. This energy-intensive process is called Proof of Work, and it’s what keeps the whole system secure.
Finding the solution is how a miner proves they’ve invested real-world resources (electricity and computing power) to validate the block. The first one to find the answer broadcasts it to the entire network. Other miners quickly check the work, and if it’s correct, the new block is officially chained to the end of the public ledger. It’s now a permanent, unchangeable part of history.
The true elegance of Proof of Work is how it makes the blockchain so incredibly secure. To tamper with an old transaction, an attacker would need to single-handedly redo all the computational work for that block and every single block that came after it—a task that is practically impossible.
For all this hard work, the winning miner gets a reward. This reward is made up of two parts: a batch of newly created coins (this is how new currency is introduced) and all the transaction fees from the block they just added. This reward is the financial incentive that keeps miners investing in expensive hardware and electricity to protect the network. You can see live data on network security and profitability, like hashrate and rewards, for top coins like Bitcoin.
Before we dive deeper, here’s a quick summary table to help lock in these core ideas.
Key Crypto Mining Concepts at a Glance
| Concept | Simple Analogy | Its Role in the Network |
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain | A shared, public accounting book | Securely records all transactions in an unchangeable chain of “pages” or blocks. |
| Miner | A digital bookkeeper and lottery player | Verifies transactions, solves puzzles, and adds new, validated blocks to the blockchain. |
| Block Reward | The prize for winning the lottery | Compensates miners with newly created coins for their work in securing the network. |
With these basics in place, we can start exploring the specific mechanics of how this all works.
How Proof of Work Powers Crypto Mining
At the heart of traditional cryptocurrency mining lies a consensus mechanism called Proof of Work (PoW). The best way to think about it is as a massive, non-stop global competition. In this contest, miners are the participants, all racing to solve an incredibly difficult cryptographic puzzle before anyone else.
This isn’t a puzzle that rewards cleverness or strategy; it’s a brute-force problem that demands raw computational power. Miners throw specialized hardware at it, making trillions of guesses every second to find a “winning number” that satisfies the network’s strict criteria. The first one to find it has effectively proven they’ve done the required computational work.
Once a miner finds that correct answer, they broadcast it across the network. Other participants, or nodes, can then very quickly check if the solution is valid. If it is, the new block of transactions gets added to the blockchain, and the race starts all over again for the next one.
This process is what keeps the whole system secure.
The crucial insight here is that security is directly linked to the amount of computational effort expended. That “mining” phase is precisely what makes the resulting blockchain so difficult to tamper with and, therefore, trustworthy.
The Key Components of Proof of Work
To really get your head around PoW, you need to understand a few core concepts. These are the gears that make the entire machine run, keeping it fair, secure, and functional.
- Hashrate: This is simply the total combined computing power of every single miner on a network. It’s measured in hashes per second (H/s), though you’ll more commonly see huge numbers like terahashes per second (TH/s). A higher hashrate means more miners are competing, which directly translates to a more secure network.
- Block Reward: This is the prize for winning the race. The successful miner gets a set amount of brand-new cryptocurrency, plus all the transaction fees included in the block they just validated. Bitcoin’s block reward is famous for being cut in half roughly every four years in an event known as the “halving.”
- Difficulty Adjustment: The network is smart. It automatically adjusts how hard the puzzle is to solve to maintain a steady rhythm of new blocks—for Bitcoin, that’s about one every 10 minutes. If more miners join and the total hashrate goes up, blocks get found too fast, so the difficulty increases. If miners leave and the hashrate drops, the difficulty decreases to compensate.
This self-regulating difficulty mechanism is the secret sauce of PoW. It ensures the blockchain’s production schedule remains predictable, no matter how many people are mining or how powerful their machines get over time.
Why Proof of Work Is So Secure
That immense computational effort isn’t just for show; it’s the bedrock of the entire network’s security. Imagine a bad actor wanted to change a transaction that happened in the past. To do that, they’d have to rewrite that block and every single block that came after it.
This means they would have to single-handedly out-muscle the combined computational power of the entire global network, re-doing all the work that has already been done. The sheer cost of the hardware and electricity required to pull this off—a feat known as a 51% attack—is so astronomically high for major networks like Bitcoin that it’s considered practically impossible.
In summary, the “work” in Proof of Work creates a powerful economic and computational wall against fraud. Each new block is like adding another heavy lock to a chain, and the collective hashrate is the only key. The more work that has been piled on, the more secure the blockchain’s entire history becomes.
Choosing Your Tools: The Essential Mining Hardware
Just like a gold prospector needs more than a pan and a prayer, a serious crypto miner needs the right gear. The hardware you pick is probably the biggest single decision you’ll make, and it can mean the difference between profit and a very expensive paperweight.
Over the years, the crypto mining world has seen its own version of an arms race. It started with people using their everyday computers, but as networks got more crowded, the game changed. We’ve moved from basic processors to hyper-specialized machines built to do nothing but mine, 24/7.

This evolution was all about one thing: rising difficulty. As more miners jumped into networks like Bitcoin, the cryptographic puzzles got exponentially harder to solve, demanding more and more raw horsepower. The tools that worked yesterday quickly became obsolete, forcing miners to find faster, more efficient ways to compete.
The Rise of GPUs
In the early days of Bitcoin, you could actually mine using a standard Central Processing Unit (CPU)—the brain inside every laptop and desktop. But it didn’t take long for miners to figure out that Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), the powerful cards built for high-end gaming, were light-years better for the job.
Why? A GPU is a master of parallel processing. It’s designed to handle thousands of simple, repetitive calculations all at once, which just so happens to be exactly what mining algorithms demand.
- Versatility: The real beauty of a GPU is its flexibility. You can program it to mine a whole host of different cryptocurrencies, from Ethereum Classic to Ravencoin, each with its own unique algorithm.
- Accessibility: GPUs are consumer products. You can walk into a store (or, more likely, order online) and buy one, making them perfect for hobbyists and smaller operations.
- Resale Value: Since they have a life outside of mining—powering games, video editing, and AI—GPUs hold their value much better than single-purpose hardware.
This adaptability makes GPUs the weapon of choice for a huge number of altcoins, especially those specifically designed to be “ASIC-resistant.” If you’re looking to build a smaller rig and explore different coins, our guide on how to start crypto mining is a great place to begin.
The ASIC Revolution
As competition got fierce, especially for kingpins like Bitcoin, the market needed even more brute force. The answer was the Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC). Unlike a jack-of-all-trades GPU, an ASIC is a machine with a single purpose in life: to solve one specific hashing algorithm at blinding speed.
An ASIC miner is the ultimate specialist. It trades away all flexibility for pure, unadulterated performance on one task. For networks like Bitcoin (which runs on the SHA-256 algorithm), an ASIC isn’t just an advantage—it’s the only way to play the game.
The market for this specialized gear is massive. The mining equipment sector was valued at $5.13 billion in 2023 and is on track to hit $6.56 billion by 2029, a clear sign of the demand for more powerful ASICs. The best new machines can achieve incredible efficiency, around 22.5 W/TH, which is about a 40% improvement in just one year. This relentless drive for efficiency is what fuels professional, large-scale mining farms.
Comparing GPUs and ASICs
So, which one is for you? The choice between a GPU and an ASIC really boils down to your goals, your budget, and what coin you’re targeting. They are two very different tools for two very different types of miners.
Here’s a quick breakdown of how they stack up.
| Feature | GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) | ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Mining a wide range of altcoins (Ethereum Classic, Monero, etc.) | Mining a single, specific algorithm (e.g., SHA-256 for Bitcoin) |
| Flexibility | High: Can switch between different mineable coins. | Extremely Low: Locked to one algorithm for its entire lifespan. |
| Initial Cost | Moderate: Can start with one card and scale up. | High: A single, modern unit can cost thousands of dollars. |
| Efficiency | Lower: Less power-efficient (hashes per watt) than an ASIC. | Very High: Optimized for maximum hashing power with minimal energy. |
| Best For | Hobbyists, small-scale miners, and those mining diverse altcoins. | Serious miners, large-scale operations, and Bitcoin mining. |
Ultimately, the hardware you choose sets the stage for your entire mining journey. GPUs provide a flexible on-ramp to the diverse world of altcoins, while ASICs are your ticket to the high-stakes, high-reward arena of professional Bitcoin mining.
Joining Forces with Crypto Mining Pools
Mining on your own can feel like a fool’s errand. For a solo miner, even one with some serious hardware, the chances of solving the next block on a major network like Bitcoin are practically zero. It’s the digital equivalent of trying to win the Powerball with just one ticket. This is precisely why crypto mining pools exist—they completely change the odds for everyone involved.
Think of it like a lottery pool at the office. Your individual chance of winning is tiny. But when you and your coworkers all chip in to buy thousands of tickets together, the group’s odds of hitting the jackpot skyrocket. When that winning ticket is found, the prize is split proportionally among everyone who contributed.
That’s a mining pool in a nutshell. It’s a collective of miners from all over the world who agree to combine their hashrate, or computational power. This massive, shared power solves blocks far more reliably than any single person could. Instead of waiting years for a massive, all-or-nothing payday, miners in a pool get smaller, steady payments.
How Payouts Work in a Mining Pool
Of course, not all pools share the winnings the same way. The method a pool uses to divvy up the rewards is known as its payout model, and picking the right one comes down to your personal appetite for risk. Some models offer predictable, stable income, while others provide a shot at higher rewards but with more volatility.
Let’s look at a couple of the most common systems out there:
Pay-Per-Share (PPS): This is the go-to for anyone who wants guaranteed income. With PPS, you’re paid a fixed rate for every valid “share” of work your machine contributes, whether the pool finds a block or not. The pool operator takes on all the risk related to mining luck.
Pay-Per-Last-N-Shares (PPLNS): This model ties your earnings directly to the pool’s success. You only get paid when the pool actually mines a block, and your cut is determined by how many shares you contributed within a recent time window. It’s a bit of a roller coaster—your income can fluctuate—but lucky streaks can lead to bigger payouts.
Key Takeaway: Your choice of payout model is a strategic one. PPS is like a steady salary, perfect for those who need predictable revenue. PPLNS is more like a commission-based job; it rewards loyalty and can be more profitable long-term if you’re willing to ride out the dry spells.
Making the right choice is a big deal. To help you figure out what’s best for your setup, check out our detailed guide on how to join a mining pool.
Comparing Mining Pool Payout Models
To really nail down the differences, let’s compare the most popular models side-by-side. Understanding the risk-to-reward profile of each is key to finding a pool that matches your financial goals.
This table breaks down common payout schemes to help you decide which model best fits your risk tolerance.
| Payout Model | How It Works | Best For | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPS (Pay-Per-Share) | The pool pays you for each valid share of work submitted, guaranteeing your income based on your hashrate. | Miners who want zero risk and a completely predictable daily income. | Very Low |
| FPPS (Full Pay-Per-Share) | A variation of PPS where the pool also pays you a share of the network’s transaction fees. | Miners seeking predictable income with a slight boost from network activity. | Low |
| PPLNS (Pay-Per-Last-N-Shares) | Payouts only occur when the pool finds a block, based on your share contributions in the last “N” shares. | Miners who are comfortable with variable income and believe in the long-term luck of their chosen pool. | Medium |
| SOLO | You use the pool’s infrastructure but are essentially mining alone. You keep the entire block reward if you find one, but get nothing otherwise. | Miners with massive hashrate who can realistically find blocks on their own but need reliable infrastructure. | Very High |
At the end of the day, joining a pool is what transforms mining from a high-stakes gamble into something that looks a lot more like a business. By teaming up, miners can smooth out their revenue and turn a wildly unpredictable process into a more consistent source of income.
Understanding the Economics of Crypto Mining
Strip away the complex technology and global networks, and you’ll find that cryptocurrency mining is, at its heart, an economic game. For anyone thinking about jumping in, the big question is always the same: can this actually make money? The honest answer is a complicated “yes, but…” It all comes down to a delicate balancing act between costs, rewards, and some very real risks.

Profitability isn’t some fixed target you can hit and forget. It’s a moving target, constantly influenced by a handful of key variables that every miner has to watch like a hawk. Getting this part right is what separates a profitable operation from a very expensive hobby.
Core Factors Driving Profitability
At the most basic level, a miner’s income is a mix of block rewards and transaction fees. On the other side of the ledger, the expenses are almost entirely dominated by hardware and electricity. The constant push and pull between these elements determines your bottom line.
Here are the main variables you’ll be wrestling with:
- Hardware Cost (CapEx): Your initial investment in ASICs or GPUs is the first, and often largest, hurdle. A single high-performance ASIC can set you back thousands of dollars, a serious upfront capital expense.
- Electricity Price (OpEx): This is the killer. It’s the single biggest ongoing cost and the most critical factor for staying in the black long-term. Measured in cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh), even a tiny difference in your power rate can completely change your financial outlook.
- Cryptocurrency Market Price: The dollar value of the coin you’re mining has a direct and immediate impact on your revenue. A roaring bull market can make even inefficient setups profitable, while a nasty bear market can sink the most optimized operations.
- Network Difficulty: As more miners pile onto a network, the puzzle gets harder to solve. This means your hardware earns less and less of that coin over time, even though it’s doing the same amount of work.
The scale of this financial ecosystem is staggering. Total global mining revenue is projected to climb to $20.4 billion in 2025, largely thanks to Bitcoin’s price and network expansion. Bitcoin alone makes up about 66% of that figure, generating roughly $13.5 billion for the miners competing to secure its network. You can dig into more cryptocurrency mining statistics like these on CoinLaw.io.
The Impact of Programmed Scarcity
Some cryptocurrencies, with Bitcoin being the prime example, have economic policies baked right into their code that directly affect miners. The most famous of these is the Bitcoin halving, an event that happens roughly every four years.
The halving cuts the block reward—the amount of new bitcoin created with each block—in half. This mechanism is designed to control the supply and create digital scarcity, but for a miner, it means your primary revenue stream gets slashed by 50% overnight.
To stay profitable after a halving, miners have to find an edge. That usually means a combination of upgrading to more efficient hardware, securing cheaper electricity, or hoping for a significant rise in Bitcoin’s price to make up for the smaller reward.
Navigating the Inherent Risks
While the potential for profit is certainly there, so are the risks. To really understand what crypto mining is from an economic perspective, you have to look at the potential downsides with both eyes open. They can be substantial.
Financial and Operational Risks
- Market Volatility: Crypto prices can swing violently. A sudden market crash can wipe out your profits in an instant, making it tough to even cover your power bill.
- Hardware Obsolescence: The mining hardware industry moves incredibly fast. A top-of-the-line ASIC today could be borderline unprofitable in just a year or two as newer, more efficient models hit the market. Its resale value tanks accordingly.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The legal landscape for mining is always in flux. A government could suddenly ban mining or impose heavy energy restrictions, forcing you to shut down or move your entire operation at a massive cost.
Ultimately, running a successful crypto mining operation is as much about sharp financial planning and risk management as it is about the technical setup. It demands careful calculation, constant attention to the markets, and a solid strategy for weathering the volatility that defines this entire industry.
The Shifting Global Landscape of Mining
Cryptocurrency mining isn’t just about technology; it’s a global industry where geography and politics are major players. The relentless hunt for the cheapest electricity and the most welcoming regulations has turned the world map of hashrate into a constantly moving target. For a long time, China was the undisputed king of this world.
Then, everything changed.
In 2021, a sweeping government ban effectively pulled the plug on the entire Chinese mining industry overnight. This event, famously dubbed the “Great Mining Migration,” triggered a mad dash as miners scrambled to find new homes for their machines. They packed up their rigs and fled to countries offering political stability and, crucially, cheap, plentiful power.
The Rise of the United States
As China exited the stage, the United States quickly stepped in to become the new global leader. States like Texas, with a deregulated energy grid and huge reserves of cheap natural gas, became hotspots for displaced operations. This mix of friendly local policies and solid infrastructure was the perfect recipe for large-scale mining farms to set up shop.
This wasn’t just a simple change of address; it marked a real turning point for the industry. The move to the U.S. attracted more serious institutional investment and signaled a push toward building more stable, long-term businesses.
The key takeaway from the Great Mining Migration is this: mining always follows the path of least resistance. Hashrate flows to regions that offer the best blend of low-cost power, clear rules, and political stability, proving it’s a remarkably mobile and adaptive industry.
By 2025, the United States has cemented its top position, leading the world in hashrate share. This is largely thanks to favorable regulations in states like Texas and Wyoming, access to cheap energy from renewables and stranded natural gas, and strong institutional backing that provides the best risk-adjusted returns for miners globally. For a closer look, you can explore a deeper analysis of the leading Bitcoin mining countries of 2025.
Other Key Mining Hotspots
While the U.S. now wears the crown, several other regions have carved out important niches for themselves in the global mining ecosystem. Each location brings something unique to the table.
Here’s a list of other major players in the global crypto mining scene:
- Canada: A top contender due to its cold climate (which drastically cuts cooling costs) and massive reserves of clean hydropower, especially in provinces like Quebec.
- Kazakhstan: It was one of the first big winners of the Chinese exodus, thanks to its proximity and cheap coal power. However, its energy grid later struggled to keep up with the new demand.
- Russia: The vast, cold expanses of Siberia offer both a natural cooling advantage and surplus energy, making it an attractive, though geopolitically complex, destination for miners.
- South America: Countries like Paraguay are quickly gaining traction. Their enormous hydropower resources offer some of the absolute lowest electricity costs on the planet.
At the end of the day, the global distribution of mining power is a direct reflection of local energy markets and government attitudes. Understanding these geographical dynamics is fundamental to grasping what mining crypto truly means on a worldwide scale.
Frequently Asked Questions About Crypto Mining
We’ve journeyed from the basics of Proof-of-Work all the way to the complex economics of the global mining industry. To wrap things up, let’s answer some of the most common questions that pop up when people first start digging into the world of crypto mining.
Can I still mine crypto on my home computer?
The short answer is no, not really—at least not for major coins like Bitcoin. While you technically could run the software, the difficulty of the network is so astronomically high that a standard PC or laptop stands virtually no chance of ever successfully mining a block.
You’d just be running up a massive electricity bill and putting a huge strain on your hardware for essentially zero reward. Modern mining requires specialized, high-powered equipment like ASICs or top-tier GPUs to even be in the running.
What’s the difference between Proof of Work and Proof of Stake?
Think of them as two different security models for a blockchain. Proof of Work (PoW), the system Bitcoin uses, is like a competition based on raw power. Miners use massive amounts of computational energy to solve a complex puzzle, and the first one to solve it gets to add the next block to the chain. It’s resource-intensive by design.
Proof of Stake (PoS), on the other hand, is more like a lottery based on investment. Participants, called “validators,” lock up their own crypto as collateral (a “stake”) for the chance to be chosen to validate transactions and create a new block. Because it doesn’t involve a computational race, PoS is dramatically more energy-efficient, though it introduces a different set of economic and security dynamics.
How much does it cost to start mining?
The price of admission varies wildly. A hobbyist looking to mine altcoins with a GPU could get started with a setup costing anywhere from $500 to a few thousand dollars.
But if you’re aiming for the big leagues with Bitcoin, you’re looking at a much steeper investment. A single, cutting-edge ASIC miner can set you back anywhere from $2,000 to over $10,000. And that’s just for the machine—you also have to account for cooling solutions and, most importantly, the ongoing, often substantial, cost of electricity.
Is crypto mining legal?
This completely depends on where you live. Mining is perfectly legal and even encouraged in many places, like the United States and much of Europe. However, other countries have placed heavy restrictions or outright banned it, citing concerns over energy consumption or financial stability.
Crucial Takeaway: The rules are always shifting. Before you spend a dime on equipment, you absolutely must research the specific laws in your country and local area. It’s the single most important step to avoid stepping into a legal or financial minefield.